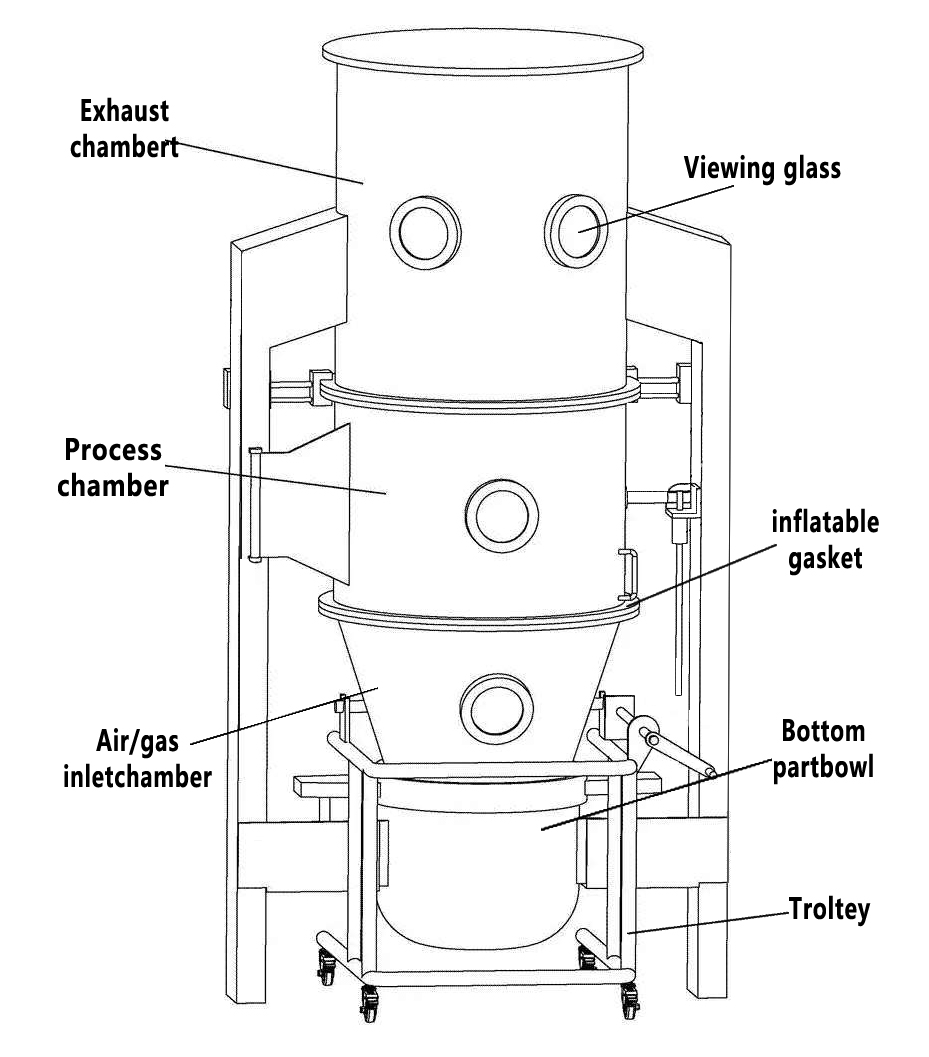
Have you ever wondered how medicines like tablets or capsules are made so perfectly and safely to use? Behind the scenes, one important step is drying the tiny particles that make up those medicines and this is done using fluidized bed dryers.

A fluidized bed dryer works by using hot air to gently lift and dry particles, almost like popcorn popping in a machine. Without proper drying, tablets could break, lose their power, or even spoil.
Want to know more? Let’s explore what a fluidized bed dryer is in pharmaceutical engineering and how it’s used.
What Is a Fluidized Bed Dryer in Pharmaceutical Engineering?
A fluidized bed dryer in pharmaceutical engineering is a machine used to dry powders, granules, and small particles that are later turned into tablets or capsules. In the machine, the hot air flows from the bottom of the container and lifts the particles, making them look like they are floating.

In pharmaceutical engineering, this is very important because medicines must stay consistent and effective. If powders are not dried properly, tablets can become weak, sticky, or even lose their strength over time.
Types of Fluidized Bed Dryers
There are several types of fluidized bed dryers. Each type suits different needs and applications.
Batch Fluidized Bed Dryer
This type processes one batch at a time. You load the material, run the drying process, and then unload it. It’s perfect for smaller quantities or when you need precise control over each batch.

Continuous Fluidized Bed Dryer
This machine runs non-stop. Material enters at one end and exits at the other after drying. It’s ideal for large-scale production where you need constant output.

Multi-stage Fluidized Bed Dryer
This design has several chambers in series. Each chamber can have different temperature and airflow settings. This allows for more complex drying processes.

Vibrated Fluidized Bed Dryer
This type adds vibration to help with fluidization. It’s useful for materials that are hard to fluidize or tend to stick together.

How Does a Fluidized Bed Dryer Work?
To understand this machine better, let’s break down the process in the exact order it happens.
Video Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dwHFKyf_ZLc
Step 1: Loading the Material

First, the wet powder or granules are placed inside the main drying chamber. Think of it like putting damp sand into a container. This is the raw material that needs drying before it can be used for making tablets or capsules.
Step 2: Starting the Airflow

Next, warm air is pumped in from the bottom through a perforated plate. This is not random air; it’s carefully heated and controlled so that it spreads evenly across the chamber.
Step 3: Fluidization Begins

Then, as the air keeps flowing upwards, the wet particles start to lift and move around. They begin to “float” and behave almost like a boiling liquid. This movement makes sure no particle stays stuck at the bottom.
Step 4: Moisture Evaporation

Now comes the actual drying. The warm air removes the water inside the particles, turning it into vapor. This vapor is carried away through the exhaust system, so that the product inside becomes drier with every passing second.
Step 5: Achieving Even Drying

Because the particles are constantly moving around, every piece gets the same amount of heat. This ensures there’s no clumping and no uneven drying, which is critical in pharmaceutical products.
Step 6: Cooling (Optional)
In many modern machines, a cooling phase is added. After drying, cool air flows in to bring down the temperature of the particles, making them safe and stable for collection.
Step 7: Collecting the Dried Product

Finally, the dried material is discharged from the chamber. At this point, the powder or granules are completely dry, uniform, and ready for the next stage, like tablet compression or capsule filling.
Key Features and Benefits of Fluidized Bed Dryers in Pharmaceutical Engineering
In pharmaceuticals, drying powders or granules properly is essential for producing high-quality medicines. Without drying, products may lose potency, stability, or even pose safety risks. For this reason, fluidized bed dryers are widely used in pharmaceutical production.
Let’s look at their key features:
1. Faster Drying Time
A fluidized bed dryer is much faster compared to traditional methods. In normal drying, materials are spread out and left for hours to dry. Here, hot air flows through the powder of granulated material and lifts it into motion, which speeds up the process.
This reduces drying time from several hours to as little as 30-40 minutes, depending on the material. Faster drying not only saves time but also increases production capacity. In fact, these machines can decrease drying time by up to 80%.
2. Uniform Drying Results
One of the biggest challenges in pharmaceutical production is making sure every particle dries evenly. If some parts are still moist, it can ruin the quality of tablets or capsules.
In a fluidized bed dryer, the constant movement of particles in hot air ensures that every granule is exposed equally. This means you don’t end up with wet spots or unevenly dried powder. Uniform drying leads to better consistency in medicines, which is critical for patient safety.
3. Temperature Control
Medicines are sensitive to heat. If they get too hot, the active ingredients may break down and lose effectiveness. That’s why fluidized bed dryers have precise temperature control systems. Operators can adjust the heat and airflow depending on the material being dried.
For instance, heat-sensitive materials can be dried at low temperatures without damaging them. This feature ensures that drying is both safe and efficient.
4. Easy Scalability for Large Batches
Another key feature is scalability. Pharmaceutical companies often need to produce small test batches first and then move to large-scale production. A fluidized bed dryer can handle both with ease.
The design allows manufacturers to dry small amounts of powder or scale up to large batches without losing quality. This makes it a flexible machine for both research labs and full-scale factories.
Applications of a Fluidized Bed Dryer
Fluidized bed dryers serve many industries with diverse applications.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Drug manufacturers use these dryers for tablets, capsules, and powders. The gentle drying process doesn’t damage sensitive compounds. It also ensures uniform moisture content, which is crucial for drug quality.
Food Processing
Food companies dry cereals, coffee beans, nuts, and spices. The process preserves flavor and nutritional value better than other drying methods. It’s also faster, which helps maintain freshness.
Chemical Industry
Chemical companies dry catalysts, polymers, and various powders. The uniform drying prevents product degradation and ensures consistent quality.
Agriculture
Farmers and processors use these dryers for grains, seeds, and fertilizers. Quick drying prevents spoilage and extends storage life.
Environmental Applications
Some facilities use fluidized bed dryers to process waste materials or remove moisture from sludge.
Challenges and Limitations of Fluidized Bed Dryers
Like any machine, fluidized bed dryers in pharmaceutical engineering come with some drawbacks too. Understanding these helps in making better decisions before investing in one.
Let’s go through the main challenges.
1. High Energy Use
Fluidized bed dryers use strong air blowers and heaters to keep powders in motion while drying them. This requires a lot of energy. Compared to simpler drying methods, they often consume more electricity. For companies running them daily, the energy bills can add up quickly.
Some newer models are designed to be more energy-efficient, but the overall power demand is still higher than that of conventional dryers. This makes energy costs a significant limitation for smaller manufacturers.
2. Not Suitable for Heat-Sensitive Materials
While fluidized bed dryers have temperature control, they are still not the best choice for materials that are extremely sensitive to heat. Some pharmaceutical ingredients lose their properties or even get damaged when exposed to hot air for long periods.
In these cases, alternative drying methods like vacuum drying or freeze-drying are used instead. So, if a product contains very delicate active ingredients, a fluidized bed dryer may not be the safest option.
3. Requires Regular Cleaning and Maintenance
Because powders and granules move constantly inside the machine, they can stick to the walls, filters, and other parts. If the dryer isn’t cleaned properly, it can lead to contamination issues, which is a serious risk in pharmaceuticals.
Regular maintenance is needed to keep the airflow smooth and the filters clear. This adds extra work for operators and sometimes means production has to pause during cleaning.
What is the Difference Between a Fluid Bed Dryer and a Fluid Bed Granulator?
| Feature | Fluid Bed Dryer (FBD) | Fluid Bed Granulator (FBG) |
| Primary Objective | To REMOVE moisture (dry the material) | To CREATE granules (agglomerate powder particles) |
| Process Vessel | Simple, usually a single bottom bowl. | More complex, with a spray nozzle installed. |
| Key Mechanism | Evaporation: Hot, dry air contacts the wet powder, carrying away moisture. | Agglomeration: A liquid binder solution is sprayed onto the fluidized powder, causing particles to stick together. |
| Input Material | Wet mass (e.g., from a wet granulation process). | Dry powder blend. |
| Output Material | Dry granules ready for compression or further processing. | Wet, agglomerated granules that usually need to be dried. |
| Product Container | Often a mobile bin that can be attached and detached. | Typically an integrated, fixed bowl within the machine. |
| Typical Use Case | The final step after a High-Shear Granulator to dry the wet granules. | An all-in-one machine that mixes, granulates, and dries in the same unit. |
FAQs
1. How does a fluidized bed dryer save time compared to other dryers?
A fluidized bed dryer reduces drying time because hot air touches every particle evenly as they float in the air stream. This makes moisture escape faster than in static dryers, often cutting drying time by half.
2. What are the limitations of a fluidized bed dryer in pharma?
Fluidized bed dryers have a higher initial cost and can cause particle attrition due to continuous movement. They are less effective for sticky or highly viscous materials, which may clump and reduce efficiency. Cleaning and maintenance can also be more complex under strict GMP requirements.
3. Do fluidized bed dryers affect the quality of the medicine?
If used correctly, no. In fact, they often improve quality because drying is uniform and controlled. However, if temperature settings are too high, heat-sensitive ingredients may lose their strength.
Ready to Upgrade Your Drying Process?
Understanding the role of a fluidized bed dryer in pharmaceutical engineering shows just how important this technology is. While it comes with challenges, its benefits in terms of performance and product quality make it one of the most reliable solutions.
But if you’re wondering where you can get one, Finetech is the right place to start.
We specialize in providing advanced pharmaceutical equipment that meets modern industry standards. Our fluidized bed dryers are designed for precision, durability, and scalability, helping brands maintain consistent quality.
Looking to improve your drying process? Contact Finetech today!