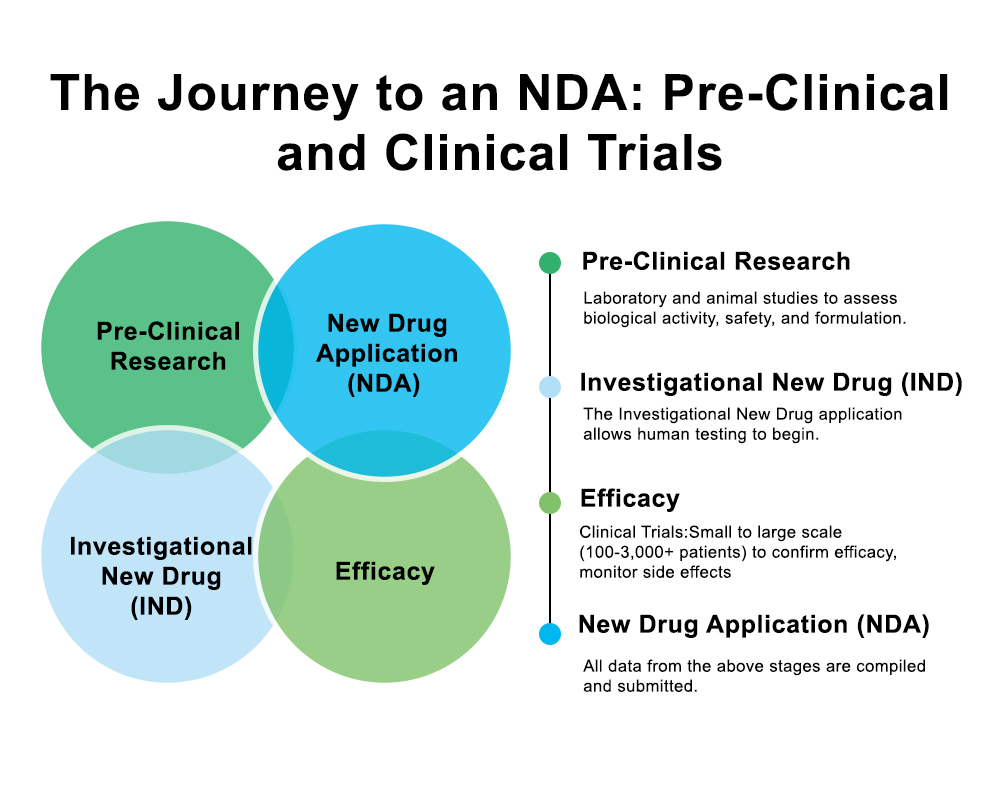
Pharma manufacturers know how quickly production challenges can spiral out of control when processes aren’t connected. A slight delay, a missing record, or a single quality issue can disrupt an entire production line and create compliance headaches you don’t have time for.

These issues often stem from a single root problem, an outdated system.
The best way to eliminate this friction is by implementing Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software. This centralized system is a comprehensive solution for managing all aspects of your pharmaceutical manufacturing facility.
Below, we’ll explain how this software works and how the right system can make your operations more efficacious, consistent, and fully compliant.
What Is Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software?
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software is a specialized digital system designed to support every step of the pharmaceutical production process. It helps manufacturers manage raw materials, track batches, and maintain compliance, all in one place.
When your team uses this type of software, you move away from scattered spreadsheets, manual checks, and reactive fixes.
In short, Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software offers:
- Provides real-time visibility into production and allows you to catch issues early.
- Stronger control over quality and compliance to pass audits without chaos.
- A unified system that connects everything from raw material arrival to finished packaging.
Types of Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software
Here’s a structured breakdown of the main types of software used in pharmaceutical manufacturing, categorized by function:
1. Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)

Core Function: Real-time tracking and control of the production process on the shop floor.
Key Features: Electronic Batch Records (EBR), work instructions, dispatching, production scheduling, labor and machine tracking.
Purpose: Ensures procedures are followed correctly, provides full genealogy and traceability from raw materials to finished goods.
2. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)

Core Function: Integrated management of core business processes across the entire enterprise.
Key Features: Inventory management, procurement, finance, sales, planning, and sometimes integrated quality modules.
Purpose: Provides the business backbone, managing resources, costs, and supply chain logistics.
3. Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS)

Core Function: Manages laboratory samples, associated data, and workflows.
Key Features: Sample tracking, test results management, stability study management, instrument integration.
Purpose: Ensures data integrity in QC labs, streamlines testing workflows, and manages specifications.
4. Quality Management Systems (QMS)

Core Function: Formalizes and manages quality processes to ensure product safety and compliance.
Key Features: Deviations, CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Actions), Change Control, Complaints, Audits, Training Management.
Purpose: Centralizes all quality events, ensures systematic investigation and resolution, and is critical for regulatory audits.
5. Process Control & SCADA Software

Core Function: Monitors and controls industrial processes at the operational technology (OT) level.
Key Features: Real-time data acquisition from PLCs and sensors, HMI (Human-Machine Interface), alarms, historical data logging.
Purpose: Automates and optimizes the physical manufacturing process (e.g., fermentation, tableting, filling).
6. Electronic Batch Records (EBR)

Core Function: Digital version of the paper master batch record, often a core module within MES.
Key Features: Step-by-step electronic instructions, operator sign-offs, data capture from equipment, and review-by-exception.
Purpose: Eliminates paper, reduces errors, and speeds up batch release.
7. Supply Chain & Logistics Software

Core Function: Manages the flow of materials, information, and finances related to pharmaceuticals.
Key Features: Demand forecasting, warehouse management (WMS), transportation management (TMS), serialization/aggregation for track & trace.
Purpose: Ensures material availability, optimizes logistics, and meets global track-and-trace regulations (e.g., DSCSA, EU FMD).
8. Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS)

Core Function: Manages the maintenance of manufacturing equipment and facilities.
Key Features: Work orders, preventive maintenance scheduling, spare parts inventory, calibration management.
Purpose: Ensures equipment reliability, reduces downtime, and maintains compliance (e.g., calibration records for GMP).
9. Data Historians & Analytics Platforms

Core Function: Collects and stores massive amounts of time-series process data for analysis.
Key Features: High-speed data storage, trend analysis, reporting, and integration with analytics/AI tools.
Purpose: Enables process optimization, continuous improvement, and supports data integrity for regulatory submissions.
10. Integrated Platforms & “One-Stop” Suites

Core Function: Combine several of the above functions (e.g., MES, QMS, LIMS) into a single, unified platform from one vendor.
Purpose: Reduces integration complexity, improves data flow, and provides a single source of truth across manufacturing and quality.
Why Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software Matters
Unplanned downtime can cost manufacturers as much as $260,000 per hour, one of the biggest hidden expenses in production.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software can help reduce these losses. It helps streamline production by automating key processes, tracking batches, and enabling better visibility across your entire line. With better software, you reduce delays and improve the way each step works.
Over time, the software strengthens batch consistency and enhances quality control, enabling more accurate production while reducing the risk of costly recalls.
Key Benefits for Pharma Manufacturers
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software becomes truly invaluable when you understand how each benefit translates into real results. Instead of offering vague improvements, it supports your daily operations in ways that directly reduce stress.
Here’s how each benefit actually impacts your facility:
1. Faster Production with Fewer Delays
When your processes are automated and connected, production moves without constant interruptions.
The software highlights bottlenecks before they slow you down and removes manual steps that usually cause delays. This leads to smoother workflows and shorter turnaround times for each batch.
2. Stronger GMP Alignment
Compliance becomes easier when documentation, audit trails, and SOPs are centralized in a single system.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software ensures every step follows GMP standards, thus reducing the risk of missed signatures, outdated forms, and inconsistent processes. It keeps your entire facility audit-ready at all times.
3. Better Decision-Making with Accurate Data
Reliable, real-time data means managers don’t have to guess what’s happening on the production floor.
Using this software, you can view the exact batch status, equipment performance, and material availability. This clarity helps leaders make faster, smarter decisions that keep production moving.
4. Lower Risk of Deviations and Recalls
Many deviations in production happen because of manual errors, missing records, or poor traceability. However, manufacturers can easily mitigate these risks by using Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software.
It guides operators through each step and automatically captures every action. If an issue appears, you can trace it instantly and fix it before it turns into a recall.
5. Improved Cost in the Long Term
With fewer delays, fewer errors, and stronger compliance, costs naturally go downward. Less material is wasted, repeat work is avoided, and the risk of costly audit findings or regulatory penalties is significantly reduced.
Over time, these improvements allow the software to pay for itself through smoother operations and increased productivity.
How to Choose the Right Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software
Choosing the right software becomes much easier when you focus on your real production needs rather than being overwhelmed by long feature lists. The goal is to pick a system that solves your problems and fits naturally into your facility’s workflow.
Let’s explore how you can choose the right software.
1. Define Your Current Challenges
Before choosing any software, list the exact issues that are causing your production to go down. This could be batch delays, documentation gaps, inaccurate inventory tracking, or frequent deviations.
When you clearly understand your pain points, it becomes easier to choose a solution that directly addresses them.
2. Match Features to Production Needs
Once you know your challenges, focus on platforms that offer features aligned with those needs. For frequent batch errors, robust batch execution tools are essential. If compliance is time-consuming, opt for automated audit trails and document control.
Matching features to problems ensures the software improves your workflow instead of complicating it.
3. Check Integration With Existing Systems
Your new Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software must integrate seamlessly with the tools you already depend on, such as ERP systems, inventory tools, lab equipment, and quality management platforms.
Strong integrations prevent data silos and reduce manual entry, which makes your entire production line more connected from day one.
4. Ask Vendors the Right Questions
Before choosing a vendor, ask about implementation timelines, training, hidden costs, update frequency, and how they handle customer support.
It’s best to request a demo customized to your workflows so you can see how the software performs in real scenarios. A confident vendor will show you exactly how their system fits your needs.
Implementation Tips for a Smooth Transition
Introducing new software into your pharmaceutical facility can make a huge difference, but only if the rollout is handled properly. Here’s how you can make the transition as smooth:
1. Build an Internal Rollout Plan
Start with a clear roadmap that outlines each phase of the implementation. Decide who will lead the project, which departments will transition first, and how progress will be tracked. A structured plan keeps the rollout organized and prevents teams from feeling overwhelmed.
2. Migrate Paper Records Properly
Many facilities still rely on paper for batch records, SOPs, and quality documentation. These need to be transferred into the new system carefully to avoid missing or inconsistent data. Take your time during migration and double-check critical documents.
3. Train Teams Early and Consistently
Training should start before the software goes live. Give your team time to learn the interface, understand new workflows, and ask questions. Once the system is active, keep training ongoing and prevent users from reverting to old manual processes.
4. Monitor Adoption and Adjust Workflows
After launch, monitor how your team is using the software. If specific steps feel slow or confusing, adjust the workflow or update permissions to make it easier. Early monitoring helps you catch issues quickly.
FAQs
1. Can smaller manufacturers afford advanced Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software?
Yes. Many vendors now offer modular systems and subscription pricing tailored for small and mid-sized manufacturers. These scaled packages include essential compliance functions without the cost or complexity of enterprise deployments.
2. What is an electronic batch record and why does it matter?
An electronic batch record is the digital version of the paper batch record. It enforces stepwise execution, captures critical process data, timestamps operator actions and produces an auditable package used for release decisions and regulatory reviews.
3. Can Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software support continuous manufacturing?
Yes. Modern systems can monitor continuous lines, capture data streams at high frequency, coordinate equipment handoffs and maintain traceability across uninterrupted production flows.
Power Your Production with High-Quality Machines
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Software reduces manual effort, improves accuracy, and keeps your operations running smoothly. Still, software alone isn’t enough. Real results come when advanced systems work alongside high-quality machinery.
This is where Finetech shines.
Our machines are built for precision, consistency, and full GMP support. They give your facility the strong technical foundation it needs to perform at its best. To date, we’ve served clients in over 60 countries, earning the trust of more than 500 satisfied clients.
If you’re ready to upgrade, schedule a quick call with our specialists today!