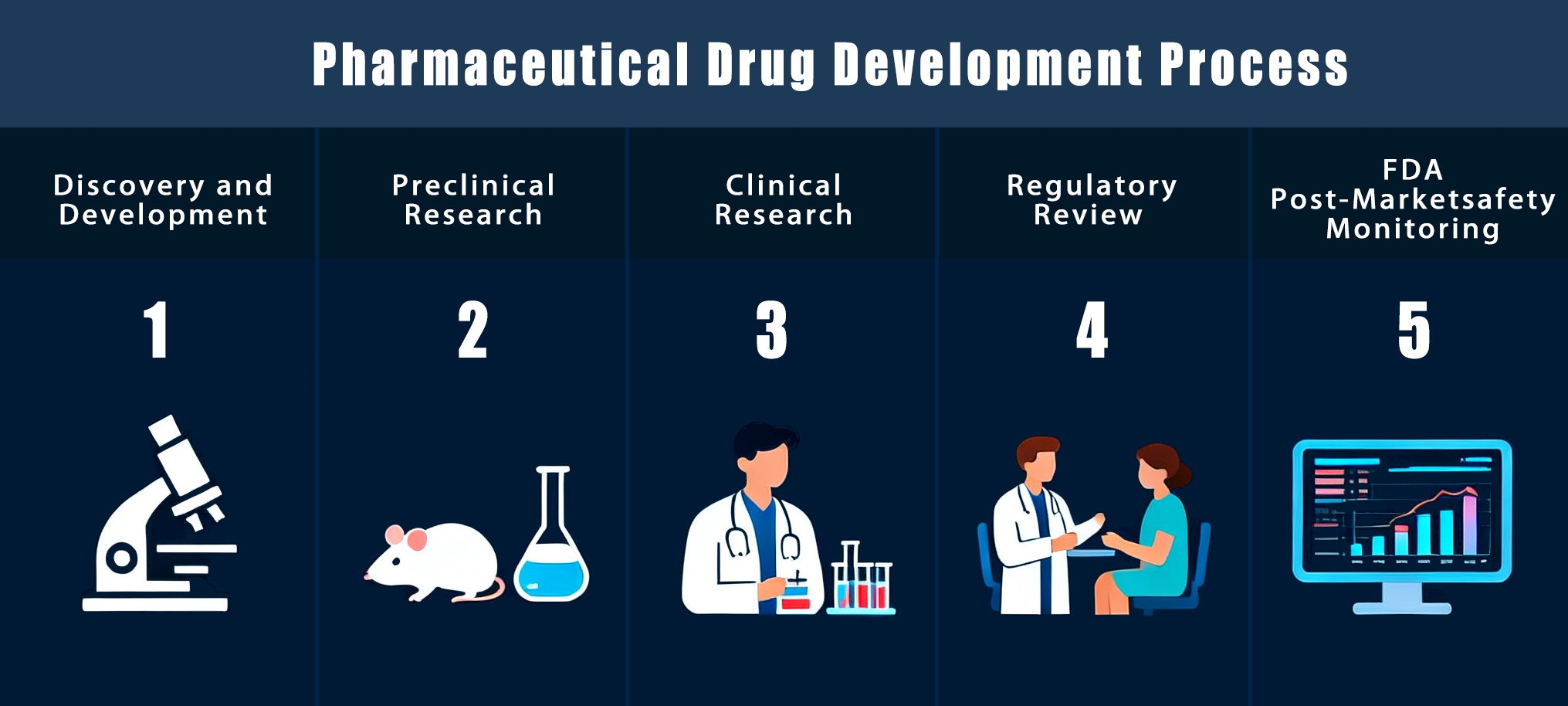
Developing a new medicine is a long and careful process. Scientists study diseases, design compounds, test them in the lab, and conduct trials to check safety and results. Each step is important to produce medicines that can help patients and improve health. In this article, we discuss the complete pharmaceutical drug development process.

First Phase of Drug Development Process: Drug Discovery
Drug discovery is the first and most important step before a medicine reaches the pharmaceutical production line. It involves finding new compounds, studying how they work in the body, and testing their safety in early stages. This stage builds the base for creating safe and beneficial medicines for patients.
Understanding the Disease
Before a new medicine can be made, scientists must first understand the disease or illness they want to treat. They study how it begins, what causes it, and how it affects the body. This helps them find weak points where a drug can work best.
By studying different patients, they also see how the disease changes from person to person. This step is very important in the pharmaceutical drug development process, as it guides the design of the medicine.
Finding Potential Drug Compounds
After understanding the disease, scientists begin searching for chemical or natural substances that might help treat it. These are known as potential drug components. Researchers test thousands of small molecules and natural extracts to identify those that can block or slow the disease process.
For example, they may test a plant-based compound that fights infection or reduces inflammation. Once a few promising compounds are identified, they are studied further to assess their safety and potency. Later, these compounds can be developed into a solid dosage formulation, like tablets or capsules, that are safe and easy for patients to take.
Choosing the Best Candidate
After testing many compounds, scientists choose the one that shows the best results and is safe to continue studying. The desired compound should perform well in lab tests and cause the least side effects.
Researchers also check how it moves, reacts, and breaks down in the body. Only the most promising and stable compound is selected for further study. This stage helps make sure that time and effort are spent on a drug that has the best chance to succeed in the pharmaceutical drug development process.
Pharmaceutical Drug Development Process
Once the most suitable drug candidate has been chosen, the focus moves from discovery to development stages. This stage involves testing the drug’s safety, studying its effects in humans, obtaining regulatory approval, and preparing it for public use. This is where the pharmaceutical drug development process officially starts.
Preclinical Research and Testing
Before a new medicine is tested on humans, it goes through preclinical research and testing. In this stage, scientists study the drug in laboratories and on animals to see how it behaves inside the body.
They check how it is absorbed, how long it stays active, and whether it causes any harm. These preclinical drug development studies help decide the right amount of drug that can be given safely in the next stage.
Importance in the Pharmacy Industry
This stage is very important in the pharmacy industry because it helps remove unsafe or weak compounds early, saving both time and cost. Only the drugs that show safe and sound results move forward to human testing.
Preclinical research and testing form a strong base for the pharmaceutical drug development process, making sure that only the safest and most promising medicines are selected for further trials.
Clinical Trials and Human Studies
The next phase of the pharmaceutical drug development process is testing the medicine on humans. After preclinical studies show that the drug is safe, it moves to the important clinical trials. These trials are done in several stages, each with a specific goal.
In the first stage, the medicine is given to a small group of healthy people to check safety and dosage. In the following stages, it is tested on patients who have the disease to see how well it works and if there are any side effects.
Step-by-Step Human Testing
Each phase gives researchers more knowledge about how the drug acts in real people. The final phase includes a large number of patients from different backgrounds to confirm results and find rare side effects.
Doctors and experts carefully observe these studies to keep volunteers safe. Clinical trials and human studies help decide whether a drug is ready for public use or needs more improvement.
Regulatory Review and Approval
After successful human testing, the medicine enters the regulatory review and approval stage. This phase checks if the new drug meets all quality and performance rules before it can be sold.
Regulatory bodies, including the FDA and EMA, carefully review reports from earlier stages of the pharmaceutical drug development process to ensure the medicine is safe and works as expected.
Main Steps in the Review Process
During this stage, companies must:
- Submit complete data on the drug’s testing, safety, and manufacturing process.
- Show that the production follows ISO standards, which confirm good quality and safety practices.
- Provide labeling, dosage, and usage information for healthcare professionals and patients.
The review process can take months or even years, depending on how complex the drug is. Only after the regulators are satisfied does the medicine receive final approval. This step protects patients and keeps public trust in the pharmacy industry by making sure every approved product meets global quality standards.
Manufacturing and Quality Control
Once a drug is approved, it moves to the manufacturing and quality control stage. In this phase, the medicine is produced on a large scale using clean and well-controlled equipment. Every step is carefully managed to make sure the product remains pure, safe, and stable.
Many companies use General Machine Products (GMP) to handle filling, packaging, and labeling processes, which help maintain consistency in the pharmacy industry.
Quality Testing at Every Stage
Quality control continues throughout the production process. Experts test samples from each batch to confirm that the ingredients and results stay consistent. The packaging is also checked to protect the medicine from light, air, or moisture.
Machines and tools are cleaned and inspected regularly to avoid contamination. This stage helps make sure the final product remains safe and of the same quality before it is sent out for patient use.
Post Market Safety Monitoring
After a new medicine is approved and sold, the work does not stop. This stage, called post-market surveillance and monitoring, focuses on watching how the drug performs once the public uses it.
Even after years of research, some side effects may appear only when a large number of people take the medicine. This phase is an important part of the pharmaceutical drug development process, as it helps keep patients safe in the long term.
Continuous Observation and Reporting
Health authorities and companies collect data from hospitals, pharmacies, and patients to track any unwanted reactions. Doctors and pharmacists are asked to report anything unusual they notice. If serious problems are found, the drug may be recalled, updated, or given new warnings. Companies also check how well the medicine continues to work.
Global Challenges in Drug Development
The pharmaceutical drug development process faces many global challenges that make it harder for new medicines to reach patients on time. These challenges slow down progress and affect how quickly life-saving drugs become available to people around the world.
High Research and Production Costs
Developing a new medicine is very costly and takes many years. Companies spend large amounts on laboratory testing, animal studies, and clinical trials before a drug reaches the market. Small companies or research groups struggle a lot to afford this process, which limits innovation.
Modern equipment, expert workers, and special materials also add to the expense. Since it can take more than a decade to bring a new drug to market, most researchers lose funding along the way. This is why only a few of the early discoveries ever become fundamental medicines.
Strict Regulatory Requirements
Every country has its own rules for approving new medicines. These rules are important for keeping patients safe, but they can make the process very slow. Agencies like the FDA in America or the EMA in Europe carefully check every detail of how a drug was made and tested.
When a company wants to sell its medicine in different countries, it must meet each one’s separate legal standards. This takes a lot of time and paperwork. Because of this, some treatments reach the market in one country while people in others are still waiting for approval.
Limited Access to Advanced Technology
Modern drug research needs strong labs, skilled scientists, digital systems, and quality testing equipment that many countries still lack. Some places do not have the right pharmaceutical machinery to test new compounds properly, while others face shortages of trained staff. Without these tools, it becomes hard to discover or produce new medicines locally.
Many researchers must send their samples abroad for testing, which slows progress and raises costs. It also limits local scientists’ chances to gain new skills. Better technology sharing between nations could help close this gap and make drug development more balanced around the world.
Unequal Access to Medicines Worldwide
Many people still cannot get the medicines they need, even after a drug is approved. High prices and weak healthcare systems are leaving millions untreated. Wealthy countries mostly receive new medicines first. Poorer ones wait years. International groups try to reduce this gap, but it still remains a big problem.
Some drug companies also focus more on products that make higher profits instead of those that meet urgent public health needs. Stronger partnerships between countries can help make lifesaving treatments available to everyone.
Ethical and Safety Concerns
Drug testing involves both humans and animals, which raises many moral questions. Researchers must treat every volunteer and test subject with care and respect. However, not all countries follow the same safety standards, and some may ignore basic rules to save time or money. This can lead to accidents or unfair treatment of participants.
There are also concerns about drug pricing. People who help in testing may later be unable to afford the medicine they helped create. Ethical responsibility should be the most important aspect of every stage of drug development, so that progress never harms those it aims to help.
Ethical and Legal Responsibilities in Drug Development
The pharmaceutical drug development process involves many stages where honesty and safety are very important. Every company and researcher has a duty to protect human life and follow laws that guide medicine testing and marketing.
Protecting Human Participants
When new drugs are tested on people, the first rule is to protect the volunteers. They must clearly understand what the study involves before they agree to join. This is called informed consent. No one should be forced or tricked into taking part. During clinical trials, their safety must come first, even if it delays research or increases cost.
Data Transparency and Honesty
All information from research and testing should be accurate and complete. Hiding negative results or changing data to make a drug look successful is unethical and illegal. Companies must report both good and bad outcomes to make sure future doctors and patients get the correct information. Honest data builds public trust and prevents harm.
Following Legal Regulations
Governments set strict rules to make sure that medicines are safe, high-quality, and properly labeled. International laws such as Good Clinical Practice and Good Manufacturing Practice define how research and production should be done. Companies that break these rules can lose their licenses or face legal action.
Fair Pricing and Accessibility
Ethics do not stop after a drug is approved. Many new drugs are too expensive for poor countries or people with low incomes. Companies have a social responsibility to make lifesaving medicines affordable and available to everyone. Fair pricing policies are what will help balance profit with public good.
Avoiding Animal Cruelty
Animal testing is sometimes necessary before human trials, but it should be done with care. Researchers should be expected to use the fewest possible number of animals and to follow humane practices. When modern alternatives like computer models or cell cultures exist, they should be preferred.
FAQs
What are DS and DP in pharma?
In pharmaceuticals, DS stands for Drug Substance, which is the active ingredient in a medicine that produces the desired effect. DP stands for Drug Product, which is the final form of the medicine that patients use, like tablets, capsules, or injections.
What are the five rules of GMP?
GMP, or Good Manufacturing Practices, guides the safe and correct manufacture of medicines. The five main rules are: use clean, proper facilities; follow correct manufacturing procedures; keep accurate records of all steps; properly train staff; and regularly check product quality.
What are NPI and NPD?
NPD, or New Product Development, is the process of researching, designing, and testing a new medicine. NPI, or New Product Introduction, is the process of launching a new medicine so patients can use it.
Conclusion
Developing a new medicine takes time, care, advanced technology, and modern equipment to keep every step safe. High-quality machines play a big part in turning research into drugs that help people. If you are looking for pharmaceutical machinery for manufacturing or packaging, contact us today for reasonable rates and on-time delivery.
Recommend Readings:
What is Solid Dosage Formulation? Simple Guide for Everyone.
How Are Medicine Tablets Made? A Simple Guide to the Manufacturing Process.