The NDA (New Drug Application) stage is often where pharma teams feel the most pressure. It’s the point where years of development, testing, and investment are formally reviewed by the FDA.
In simple terms, an NDA in pharmaceuticals is the document a company submits to the FDA to request approval for a new drug. This is a significant milestone in any drug development journey.
So, if you’re developing a new formulation or preparing to scale production, you need to understand how the NDA submission process works. And that’s precisely what we’ll be focusing on today. Let’s get into it.
What Is an NDA in Pharmaceuticals?

An NDA is the official request a pharmaceutical company submits to the FDA to get approval to market a new drug. It is the final step in the drug development process and includes everything the FDA needs to decide whether the medicine is safe and helpful.
However, the process is quite demanding. That’s why only about 1 in 10 drugs that enter clinical trials ever make it to approval. This number illustrates the challenges of the path and highlights the significant role the NDA plays.
An NDA acts like a complete “story” of the drug. It contains:
- All clinical trial results
- Complete data on safety and effectiveness
- Details about how the drug is made
- Quality control and stability information
- Packaging, labeling, and proposed usage instructions
The FDA reviews this information to confirm that the benefits outweigh any risks. Moreover, it proves that the manufacturing process can consistently produce a safe and reliable product.
Purpose of an NDA in Pharmaceuticals
The primary purpose of an NDA is to demonstrate that a new drug is safe, efficacious, and consistently manufactured with high quality.
The FDA uses this application to confirm that every part of the product, from its clinical data to its manufacturing process, meets strict standards. One of the biggest reasons for this requirement is to catch issues early.
An NDA also exists to protect patients from inconsistent or unsafe products. It gives the FDA a clear view of how the drug is produced and whether the pharmaceutical equipment and processes behind it can deliver the same quality in every batch.
Key Components of an NDA
An NDA in pharmaceuticals includes several major sections that provide the FDA with a comprehensive picture of how a drug performs. Here are the components you must be aware of if you’re looking to meet this requirement.
1. Clinical Data Package
The clinical data package includes all results from Phase 1, 2, and 3 trials. These studies demonstrate how the drug behaves in the human body, its effectiveness, and potential risks that may arise during actual treatment.
This section also contains all safety assessments and detailed reports of any adverse events that happened because of the new formulation.
2. CMC (Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls)
CMC is one of the most important parts of an NDA because it explains exactly how the drug is made. It covers information about the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), including its quality standards.
Moreover, this component describes the manufacturing process, from raw materials to finished product. With this information, the FDA can determine whether the drug can be produced consistently and safely at large scales.
3. Labeling and Packaging
This section outlines the proposed drug label and all instructions that will accompany the product. This includes dosage guidelines, usage directions, warnings, and safety information.
Clear labeling and serialization are essential for patient safety and guarantee that healthcare providers know exactly how to administer the drug. The FDA reviews this content carefully to make sure it is accurate.
4. Administrative and Legal Requirements
The final part of an NDA in the pharmaceutical industry covers key legal and administrative documents. In this step, you are required to provide patient certifications, proof of user fee payments, and other required regulatory documents.
It also includes compliance forms confirming that the company meets all FDA and legal obligations.
How Does the NDA Submission Process Work?
Submitting an NDA is a structured process that helps guarantee the FDA receives complete, accurate, and high-quality information.
Here are the steps that you must follow to be compliant:
1. Pre-NDA Meeting with the FDA
Before submitting an NDA, most companies schedule a pre-NDA meeting. This meeting gives both sides a chance to review the final clinical results, manufacturing data, and any remaining concerns.
It also helps clarify what the FDA expects in the application, which eventually reduces the risk of delays in the future.
2. Preparing the Full Documentation Package
Once the plan is aligned, the company compiles all required data, including clinical results, CMC information, labeling drafts, and administrative forms.
This step requires coordination between regulatory, manufacturing, quality, and clinical teams. Always remember, a well-organized package increases the chances of a smooth review.
3. Submitting Through the FDA Electronic Gateway
The NDA is finally submitted electronically via the FDA’s online system called ESG NextGen. Make sure the file adheres to strict formatting rules so the FDA can process and review it. Once submitted, the application enters the FDA’s internal screening pipeline.
4. In-Depth FDA Review
After the review is filed, the FDA begins a detailed evaluation of all data. Reviewers assess clinical performance, manufacturing quality, safety information, and labeling accuracy.
During this stage, the FDA often sends questions or requests for clarification. Companies must respond quickly and clearly to avoid delays.
5. Final Decision and Approval
If the data support safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing consistency, the FDA issues an approval letter. However, if the FDA identifies major issues, the agency may issue a Complete Response Letter outlining what needs to be corrected.
Once you make the changes and gain approval, it means your product can now be marketed in the U.S.
How Long Does the NDA Approval Process Take?
The NDA approval timeline depends on the type of review the drug receives. For most products, the FDA follows a standard review, which typically takes around 10 to 12 months from the time the application is accepted.
Though there are some cases when a drug qualifies for priority review, if that happens, the approval time is cut almost in half to about 6 months. Priority review is only given to drugs that offer major improvements in treatment or address serious medical needs.
FAQs
1. How is proprietary or confidential information protected during NDA review?
The FDA treats much of the clinical and CMC data in an NDA as confidential business information. Public summaries and approved labeling are released, but raw datasets and proprietary manufacturing details remain protected under statutory confidentiality provisions.
2. What is an approvable letter or complete response letter?
If the FDA cannot grant approval as submitted, it issues a complete response letter that describes deficiencies and required actions. An approvable letter outlines conditions that must be met before approval. Sponsors respond with amendments, new data or proposals for risk management.
3. When do patents and exclusivity matter in an NDA?
Sponsors submit patent information and may seek regulatory exclusivities that delay generic entry for defined periods. Patent listings in the NDA also support patent certification processes for later generic applicants. Exclusivity types include new chemical entity exclusivity, pediatric exclusivity and orphan exclusivity among others.
Don’t Let Your NDA Slip Away with Wrong Machinery
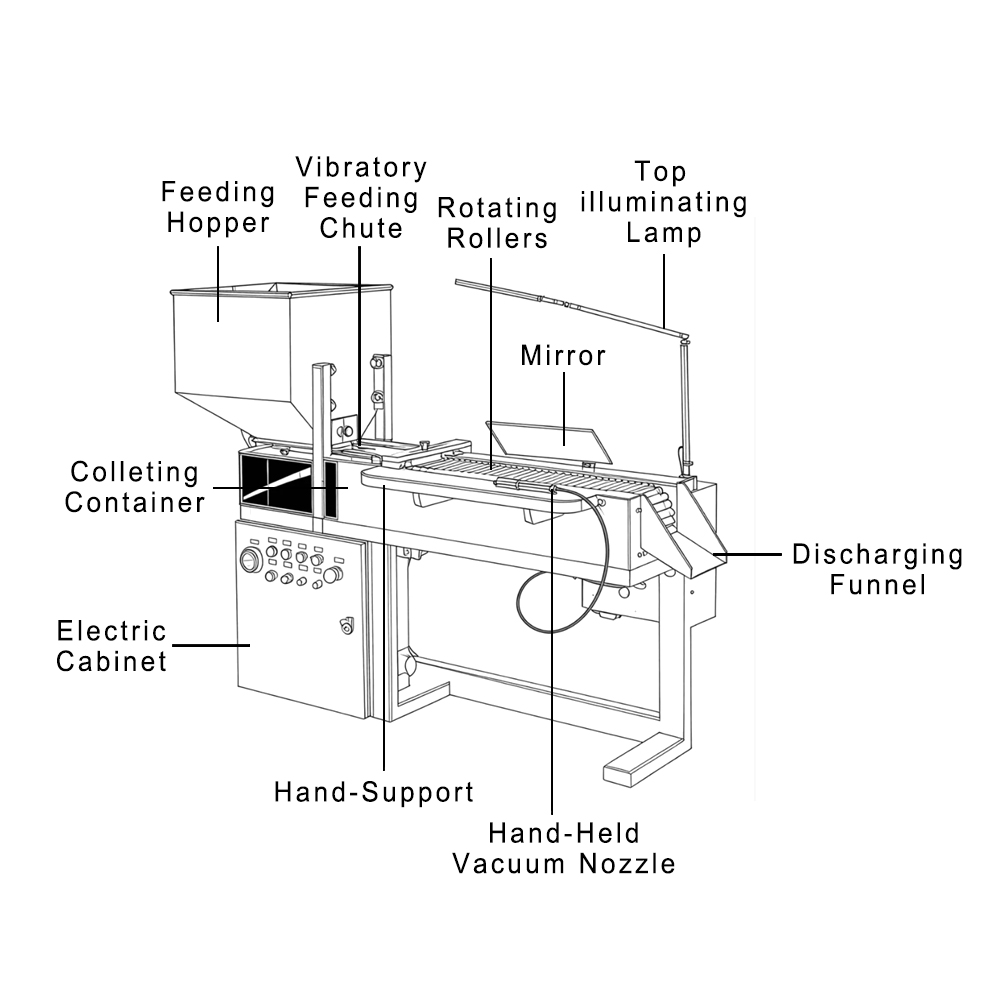
Submitting an NDA in the pharmaceutical industry is a major milestone, but approval depends on more than clinical data alone. One of the most important things the FDA looks at is the quality of the machinery you’re using. This shows the importance of having reliable suppliers like Finetech.
Our pharmaceutical machinery is designed to support reliable, compliant production at every step of the process. In fact, manufacturers across 60+ countries and 500+ clients trust Finetech because we deliver equipment that strengthens the technical foundation required for FDA approval.
If you’re stuck due to machinery, hop on a quick call with our specialists today!